What is Elasticity of Demand
Price elasticity of demand (PED or Ed)
Measure used to show the responsiveness, or elasticity, of the quantity demanded of a good or service to a change in price.
Devised by Alfred Marshall, using the ceteris paribus (all other things being equal) assumption, price elasticity shows by how much quantity changes as a result of a change in price. (Disregard the negative)
Formula
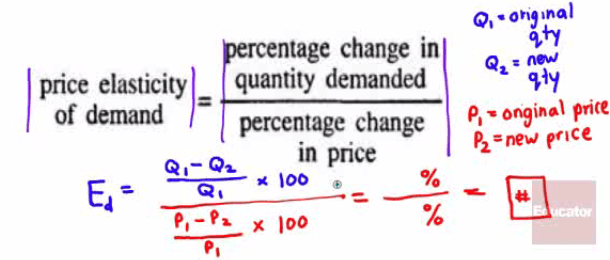
How to remember
- Queen is greater than the Princess
The Variety of Demand Curves
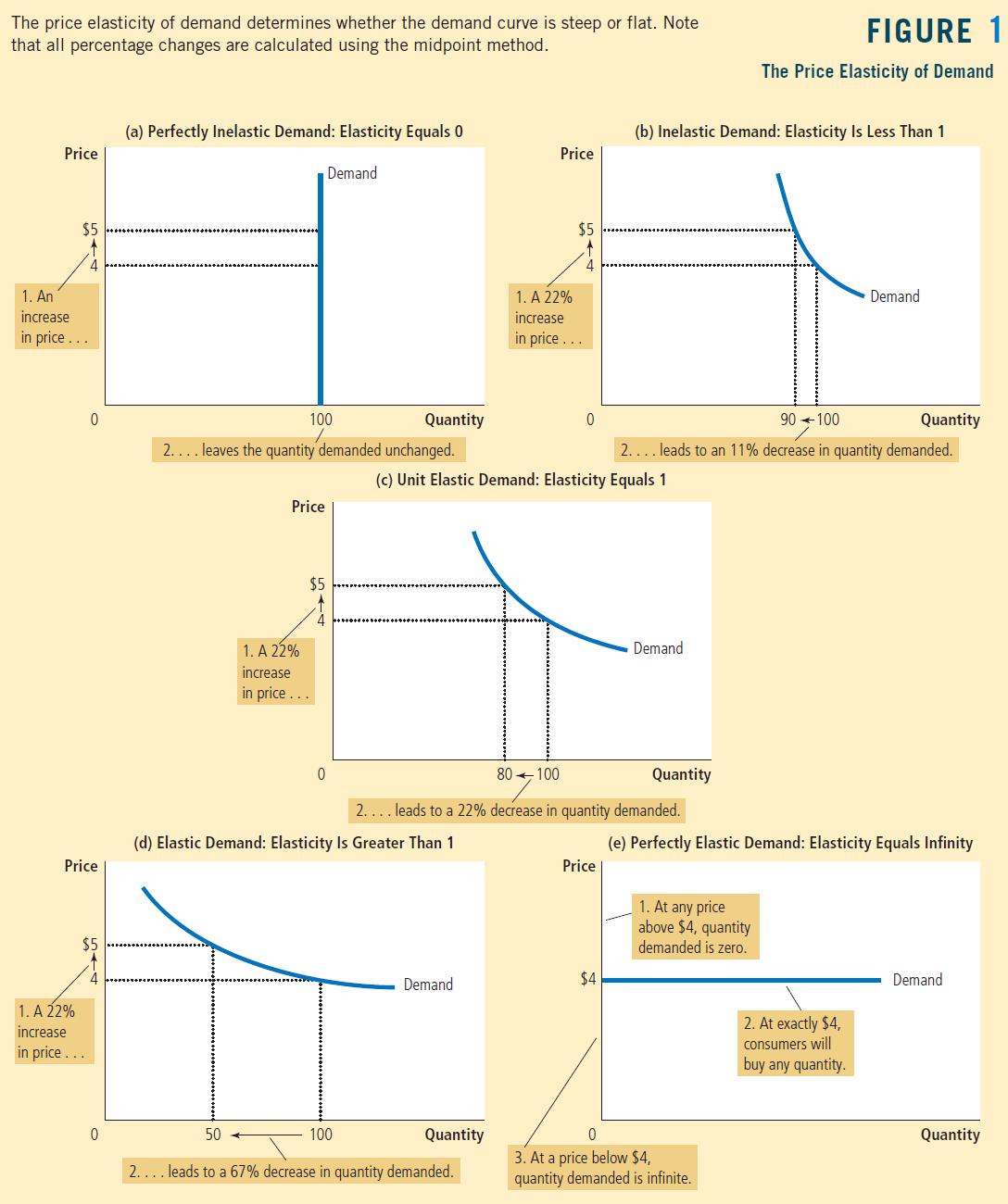
Elastic Demand
When e > 1, demand is elastic, or the percent change in quantity is greater than the percent change in price.
It means that the product is relatively price-sensitive
ie. fast-food restaurants, fruits, haircuts
Demand curve is relatively flat.
Inelastic Demand
When e < 1, demand is inelastic, or the percent change in quantity is less than the percent change in price.
It means that the product is not very sensitive to a change in price
ie. gasoline, insulin
Demand curve is relatively steep.
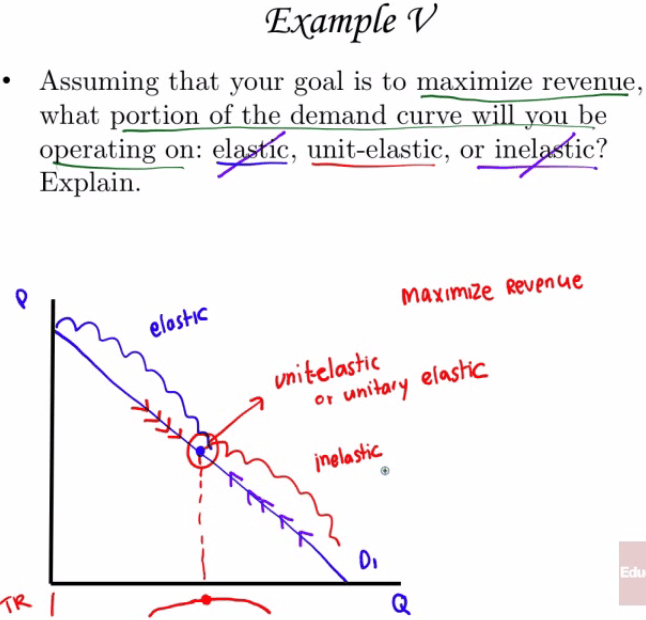
Price Elasticity of Demand and Total Revenue
The total amount paid by buyers, and received as revenue by sellers, equals the area of the box under the demand curve.
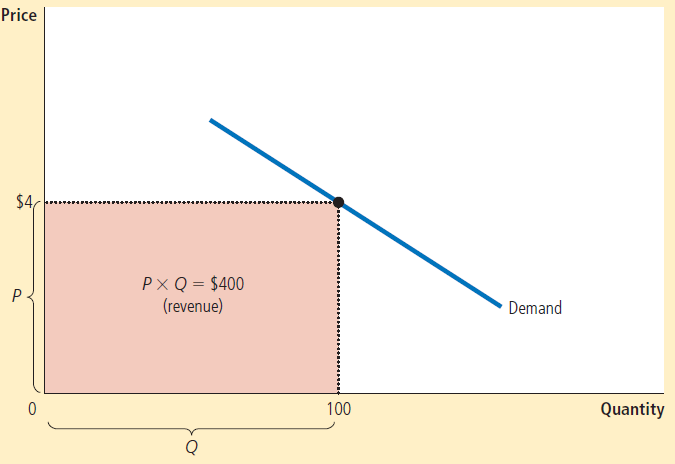
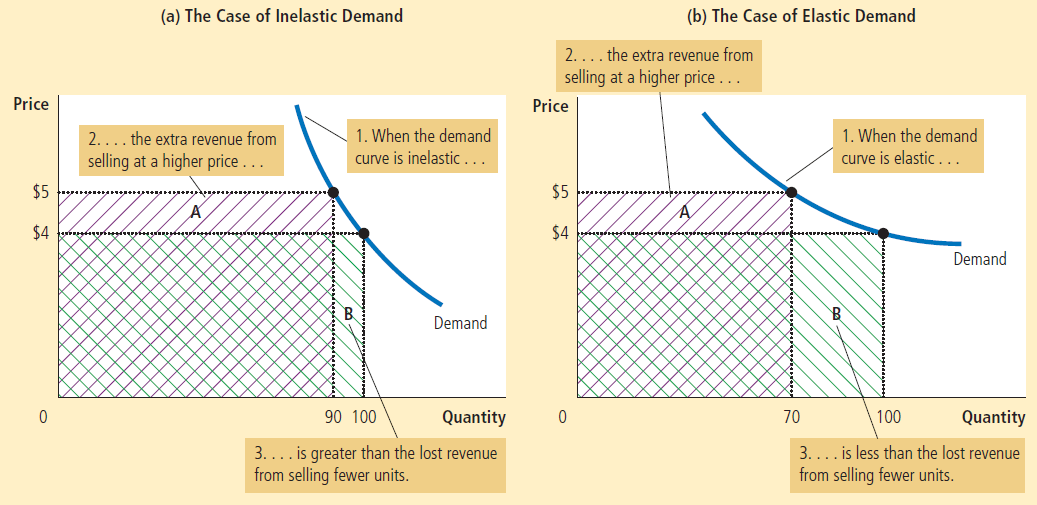
When demand is inelastic (e < 1), price and total revenue move in the same direction:
- If the price increases, total revenue also increases.
When demand is elastic (e > 1), price and total revenue move in opposite directions:
- If the price increase, total revenue decreases.
If demand is unit elastic (e = 1), total revenue remains constant when the price changes.
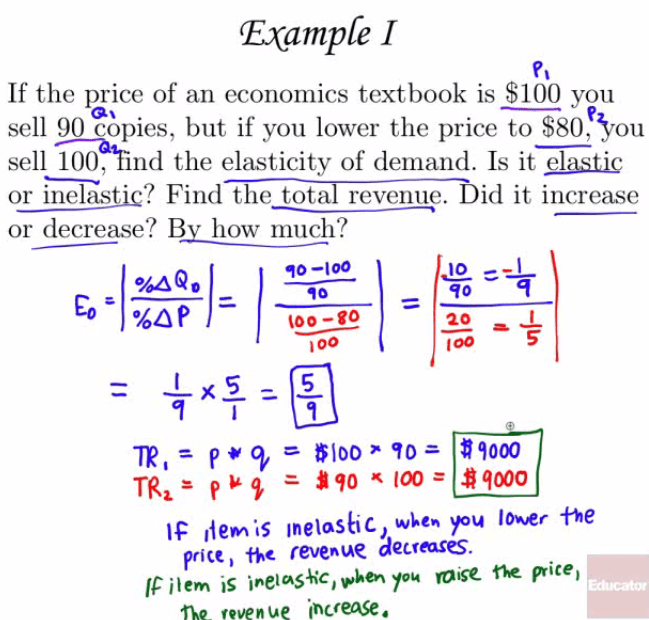
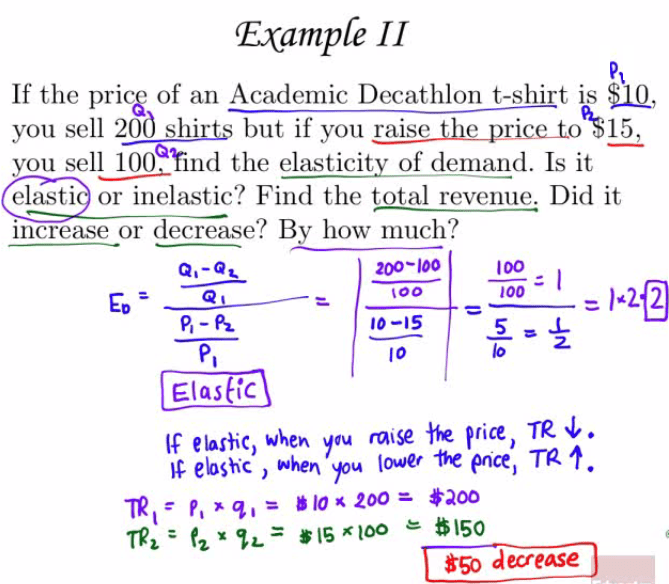
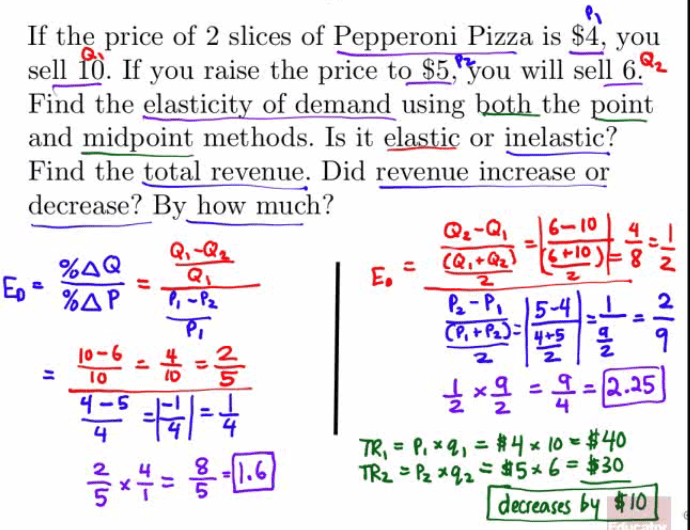
Examples
Midpioint Method to Find Elasticity
Definition
![One way to avoid this problem is to use the midpoint method for
calculating elas- ticities. The standard procedure for computing a
percentage change is to divide the change by the initial level. By
contrast, the midpoint method computes a per- centage change by
dividing the change by the midpoint (or average) of the initial and
final levels. For instance, $5 is the midpoint between $4 and $6.
Therefore, ac- cording to the midpoint method, a change from $4 to $6
is considered a 40 percent rise because (6 4) / 5 X 100 40. Similarly,
a change from $6 to $4 is considered a 40 percent fall. Because the
midpoint method gives the same answer regardless of the direc- tion of
change, it is often used when calculating the price elasticity of
demand between two points. In our example, the midpoint between point
A and point B is: Midpoint: Price = $5 Quantity = 100 According to the
midpoint method, when going from point A to point B, the price rises
by 40 percent and the quantity falls by 40 percent. Similarly, when
going from point B to point A, the price falls by 40 percent and the
quantity rises by 40 percent. In both directions, the price elasticity
of demand equals 1. The following formula expresses the midpoint
method for calculating the price elasticity of demand between two
points, denoted (Q, PI) and (Q, P2): Price elasticity of demand — - +
PI)/2\]](media/image59.png)
Comparison
Factors That Determine Price Elasticity
Whether close substitutes are available
Tends to be high if consumers are willing to replace with substitutes.
Tends to be low if there are no close substitutes
Whether the good is necessity or a luxury
- Life-saving medication will be inelastic but things you can live without tend to be elastic
Time
PED tends to increase over time
ie. demand for gas is more elastic as behavior changes
Share of income spend on the good
Elasticity of demand tends to be low when prices are lower
Conversely, PED is higher when prices are higher
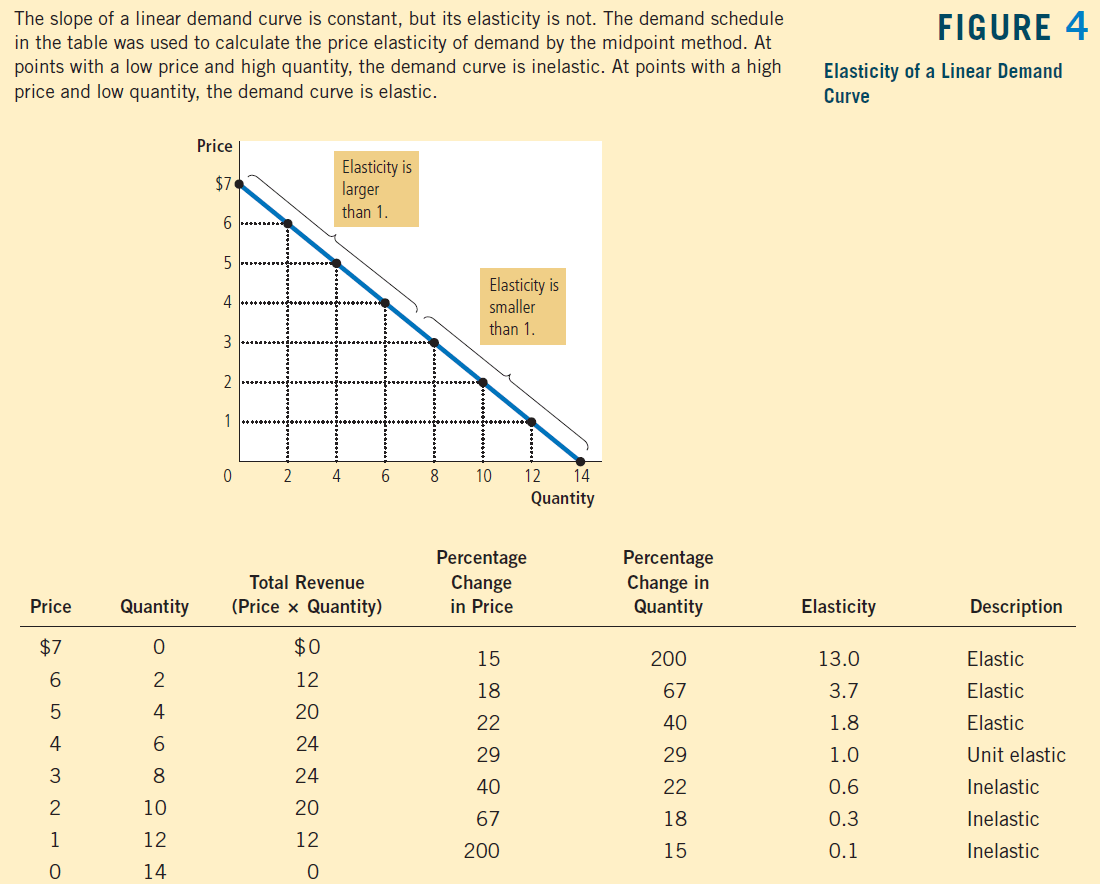
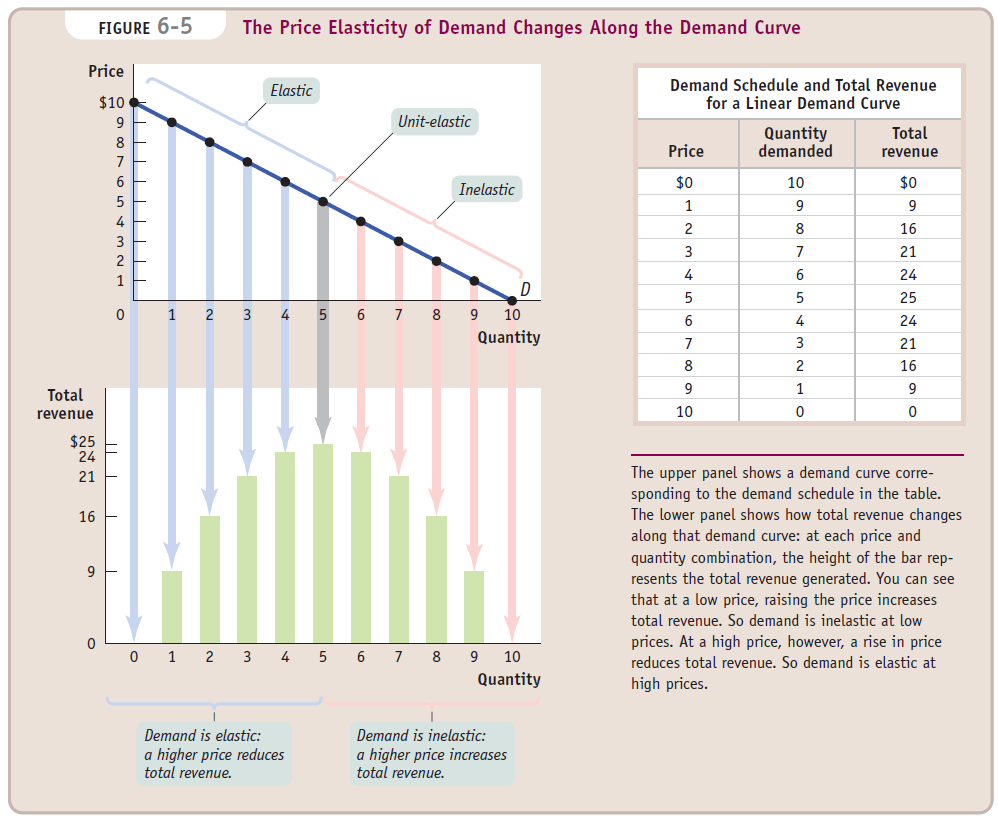
Price Elasticity Along the Demand Curve
- Price and total revenue
| Inelastic | Price↑ | Total Revenue↑ |
|---|---|---|
| Inelastic | Price↓ | Total Revenue↓ |
| elastic | Price↑ | Total Revenue↓ |
| elastic | Price↓ | Total Revenue↑ |
- Graph
Example